March 20, 2025, PHDEC conducted a webinar on “Panama Disease of Banana: Advancing Knowledge and Research for Sustainable Disease Management Solutions.” The webinar aimed to educate growers and farmers about Panama wilt disease, its symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Panama disease is a highly destructive fungal disease that poses a significant threat not only to Pakistan’s banana industry but also to major banana-producing countries worldwide. Farmers require comprehensive guidelines to identify, diagnose, and manage the disease using recommended agricultural practices.
To address this critical issue, PHDEC engaged experts from Sindh Agriculture University, Tandojam, who have conducted extensive research on Panama wilt disease. Dr. Rehana Naz Syed, Professor, Department of Plant Protection, Sindh Agriculture University, delivered a detailed presentation on banana orchard management, Panama wilt disease, its symptoms both external and internal, and its control measures.
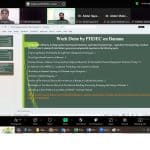
She emphasized that there is no cure for Panama disease once it infects a field, as it is a soil-borne disease. The only effective approach is to remove and destroy infected plants to prevent further spread. Therefore, she stressed to keep monitoring and be vigilant to identify the disease. Dr. Syed shared a standardized protocol for managing Panama disease, which includes:
- Cutting off pseudo stems 10 cm above the growing point without disturbing the soil.
- Chopping pseudo stems and leaf material into 60–80 cm pieces and sealing them in heavy-duty plastic bags.
- Adding 1 kg of urea per bag, sealing securely, and placing them in the destruction zone.
- Gouging out the surface of each remaining corm to create a hollow and injecting it with:
o 5 mL glyphosate solution (90 g active per liter of water).
o 18 mL imidacloprid solution (200 mL per 100 mL water). - Spraying each stool and the surrounding 30 cm area with 500–750 mL bifenthrin solution (66 g active per 100 L water).
- Applying 200 g of urea evenly on the gouged surface of each corm.
- Applying 1 kg of urea per m² around each infected stool and covering the destruction zone, including plant material bags, with high-grade plastic sheeting, securing it properly.
The session concluded with an interactive Q&A segment, where participants actively engaged with the experts.
A large number of growers, farmers, R&D professionals, entrepreneurs, and academia attended the webinar and appreciated PHDEC’s initiative in addressing this critical issue.